Understanding GaN Chargers: Pros and Cons
GaN chargers, an emerging charging technology, have gained significant attention in the market due to their unique advantages. They offer remarkable convenience in our daily lives with their compact size, efficient performance, and stable operation. So, what makes GaN chargers special, and how do they enhance the charging experience? Let's delve into the pros and cons of GaN chargers and their future applications.
Key Takeaways on GaN Chargers
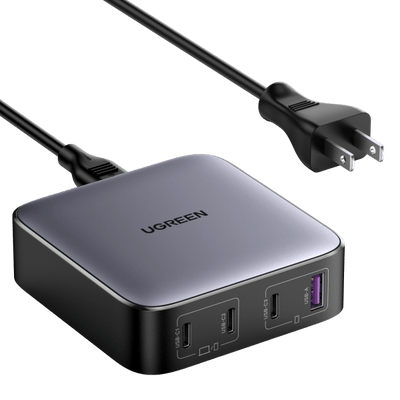
1.High Efficiency and Compact Design: GaN chargers use gallium nitride, a material that allows for higher energy conversion efficiency and smaller sizes, making them perfect for modern, portable devices.
2.Fast Charging and Energy Efficiency: Thanks to GaN’s superior properties, these chargers deliver faster charging speeds and reduce energy waste, appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
3.Enhanced Safety Features: GaN chargers excel in thermal management, reducing heat buildup and the risk of fire hazards, ensuring a safer charging experience.
4.High Cost as a Barrier: Despite their benefits, the high manufacturing cost of GaN chargers results in higher prices, limiting their appeal to budget-conscious buyers and mid-to-low-end markets.
5.Promising Future Applications: With the rise of 5G and electric vehicles, GaN chargers are well-positioned to meet the growing demand for efficient, high-power solutions in these sectors.

What is GaN?
Gallium Nitride (GaN) is a novel semiconductor material and more environmentally friendly than traditional silicon-based chargers that offers unique properties like a wide bandgap, high electron saturation velocity, and excellent thermal conductivity. Compared with traditional silicon materials, gallium nitride is more suitable for manufacturing electronic devices with high efficiency, high power density, and high-temperature operation. In the realm of chargers, the application of GaN technology enables smaller sizes, higher efficiency, and better safety.
Pros and Cons of GaN Chargers
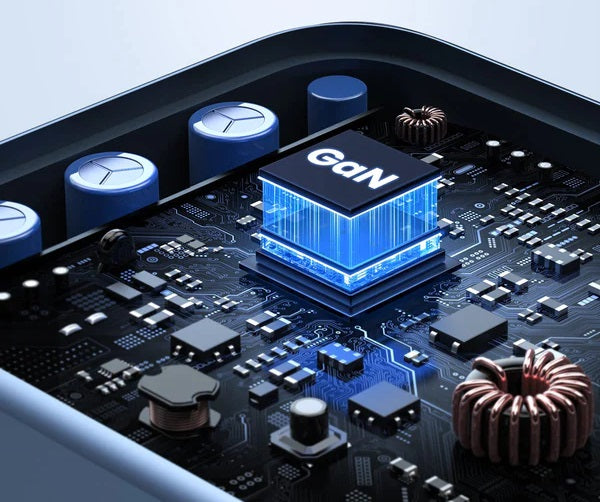

Pros: High Efficiency, Compact Size, Fast Charging, Energy Efficiency, Enhanced Safety, Wide Compatibility
GaN chargers stand out in the market due to several noteworthy advantages. Their advanced semiconductor material enables higher electrical energy conversion efficiency. This means that under the same power output, GaN chargers generate less heat and can be more compact, seamlessly integrating into compact devices to meet modern portability demands.
Thanks to the superior properties of GaN materials, GaN chargers offer faster charging speeds. This eliminates long waits during charging sessions, enhancing convenience. The efficient energy conversion and compact size contribute to reducing energy waste and environmental impact. This is particularly relevant in our increasingly eco-conscious society.
GaN chargers boast exceptional thermal management and safety features. They effectively control temperatures over long periods, reducing fire hazards and providing users with a more secure charging experience. As technology continues to evolve, GaN chargers are not only suitable for a range of electronic devices but also demonstrate wide compatibility.
This means users can effortlessly switch between devices without the need to change chargers, further enhancing convenience.
Cons: High Cost
The main downside of GaN chargers lies in their cost. The sophisticated synthesis and manufacturing process of GaN materials results in relatively high prices for GaN chargers. This can limit their widespread adoption in the mid-to-low-end market, making them less appealing to budget-conscious consumers. Additionally, their current market positioning targets high-end consumers and performance seekers, limiting broader consumer acceptance.
Future Applications of GaN Chargers
Thanks to emerging charging technologies, GaN chargers have been quickly embraced by digital manufacturers. Well-known phone brands and third-party accessory providers have eagerly launched GaN chargers to meet market demand. With the upcoming rollout of 5G technology and the expanding electric vehicle market, the future prospects for GaN chargers are incredibly promising.
5G base stations and electric vehicles require efficient and high-power density power delivery solutions, making the small size and efficient nature of GaN chargers highly suitable for these applications. As technology continues to advance and costs decline, GaN chargers are expected to become more widely adopted in the consumer electronics market, playing a pivotal role in future applications.

Conclusion
In conclusion, GaN chargers offer numerous advantages as an emerging charging technology. However, there are also some drawbacks that need to be addressed. As technology continues to evolve and costs decrease, GaN chargers are poised to play an even more significant role in various applications in the future.

































